TMR Theory and Hypothesis
2021, Volume 4 Issue 3
TMR Theory and Hypothesis,关注传统医学和民族医学理论的现代研究。旨在发表将这两种理论与现代生物医学,物理学,化学和数学模型相结合的创新文章。目前已被ScienceOpen,Ingenta Connect,J-Gate,中国科技期刊数据库(CSTJ),超星期刊数据库和Google学术搜索、知网空间、EuroPub收录。TMR Theory and Hypothesis 特为优秀稿件开通快速发表的绿色通道,审稿1-2周,Online周期4周。
-01-
柏正平从气、痰、瘀论治胃癌
This paper will introduce the clinical experiences of Professor Zheng-pingBai in treating gastric cancer. In his diagnosis and treatment of this disease, Professor Bai advocates the integration of disease, symptom, and syndrome differentiation, pointing out that gastric cancer is caused by the accumulation of phlegm-dampness and blood stasis in the stomach due to qi stagnation. Therefore, the basic pathogenic mechanism involves the loss of harmonious descent in the stomach. This implies that treatment should prioritize qi activity by calming the stomach and suppressing the abnormal ascent of qi, as well as emphasizing theelimination of phlegm and stasis,and this has achieved significant therapeutic efficacy.

-02-
从肺、脾、肾三脏探究水液代谢
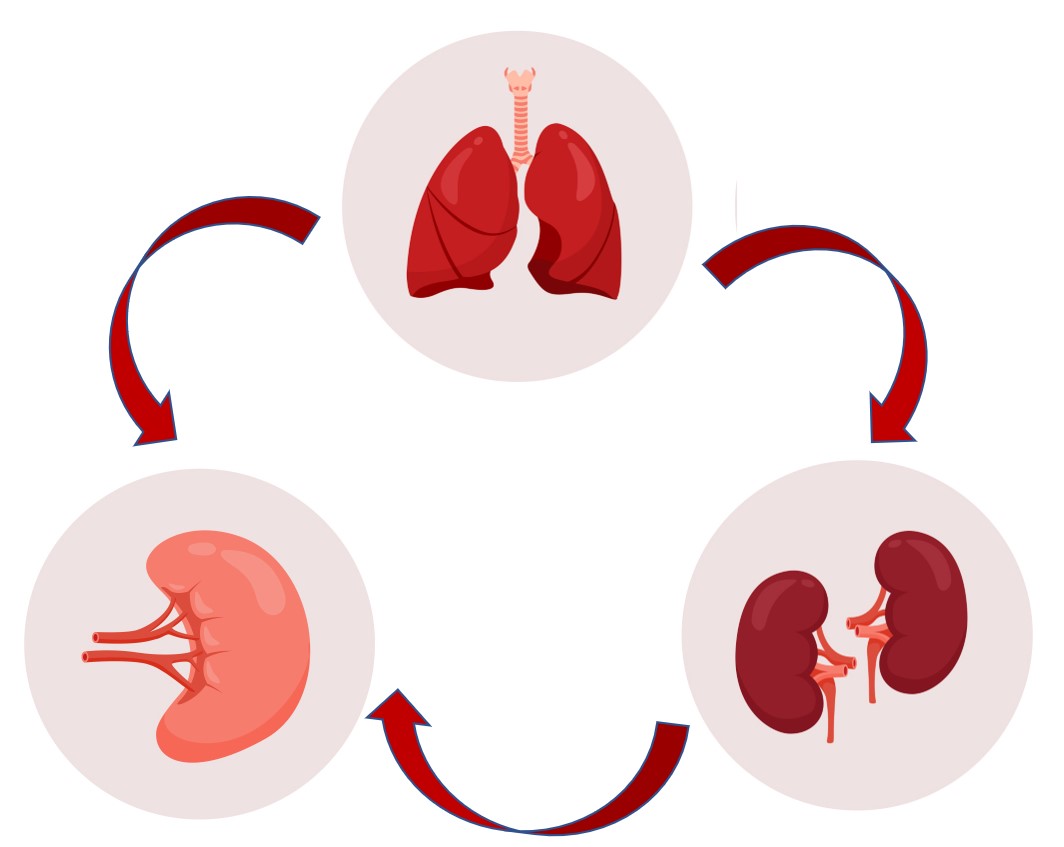
Water and liquid are the material basis of human metabolism. Traditional Chinese medicine believes that water and liquid metabolism is a very complex process that requires the synergy of the internal organs, but mainly the physiological functions of the lungs, spleen and kidneys. If the function or structure of the spleen, lungs, kidneys, or triple-burner is abnormal, it is easy to cause abnormalities in the body's water metabolism, which in turn leads to the production of pathological products such as damp phlegm.
-03-
中药药理指导下自身免疫性溶血性贫血的多靶点干预探析
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA) is a rare and refractory acquired autoimmune disease.At present, western medicine treatment has obvious side effects, low drug sensitivity, easy to relapse and other problems.Multi-target treatment of autoimmune hemolytic anemia through the study of pharmacology of traditional Chinese medicine can effectively improve the clinical efficacy of autoimmune hemolytic anemia, and the price is low, worthy of promotion.This paper discussesthe effects of traditional Chinese medicine on maintaining acid-base balance, alleviating liver and kidney function damage and immune collapse.

-04-
论结、代脉与“缓慢型心律失常”的关系
Pulse diagnosis is an important basis for the diagnosis of Chinese medicine. It is the rich experience accumulated by the predecessors in the long and continuous practice, and it is a unique diagnosis method of Chinese medicine. There are many names of pulse conditions in traditional Chinese medicine. The four elements are analyzed and summarized in terms of position, number, shape, and momentum. The four elements are used as 28 kinds of pulses. Among them, the regularly intermittent pulse and the intermittent pulse are characterized by arrhythmia and intermittent stop of the pulse. Intermittent pulse means irregular intervals;when a pulse comes, Regularly Intermittent pulse have regular stops. This kind of phenomenon is similar to the bradyarrhythmia in modern medicine. The knot pulse is an irregular pulse stopping, which can be seen clinically in sinus arrest, second-degree type I sinus block, second-degree type I atrioventricular block, and escape beats and so on . On the other hand, Regularly Intermittent pulse is a regular pulse stopping, which can be clinically found in the second degree type II sinus block, the second degree type II sinus block, and the second degree type I atrioventricular block with a special 2:1 type of atrioventricular block type and so on.

-05-
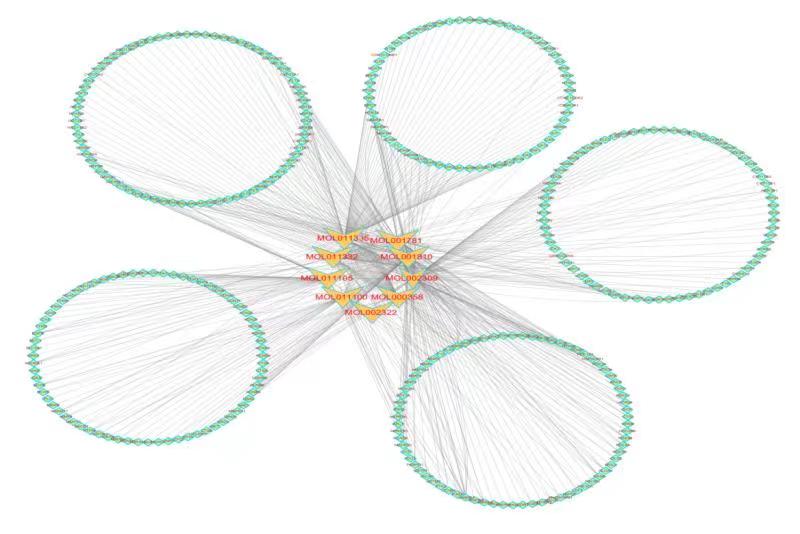
通过综合药理研究探索青黛治疗骨髓增生异常综合征的分子机制
Oral administration of indigo naturalis (IN) is used as a complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) regimen for the treatment of myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). However, its mechanism of action has not been fully elucidated and needs to be further explored. Methods: By searching the traditional Chinese medicine system and analyzing platforms (TCMSP), bioinformatics analysis tool for the molecular mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine (BATMAN-TCM), and Swiss Target Prediction network database, the main active components and potential targets of IN were obtained. Based on this, a component-target network was established by Cytoscape 3.6.1 software. Differentially expressed genes (DGEs) in MDS were obtained from three GEO (Gene Expression Omnibus) gene chips. Then, the protein-protein interaction (PPI) network of DGEs was constructed and analyzed by STRING database and Cytoscape 3.6.1 software. In addition, Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) biological enrichment analysis were carried out using REVIGO and KEGG Orthology Based Annotation System (KOBAS) on DGEs, respectively. Identification of IN-MDS compound targets was performed by matching potential targets of active components with disease-related targets. The results of KEGG pathway enrichment analysis were combined with compound targets to screen key targets. In the end, molecular docking was performed by SYBYL-X2.1 to verify the key targets.